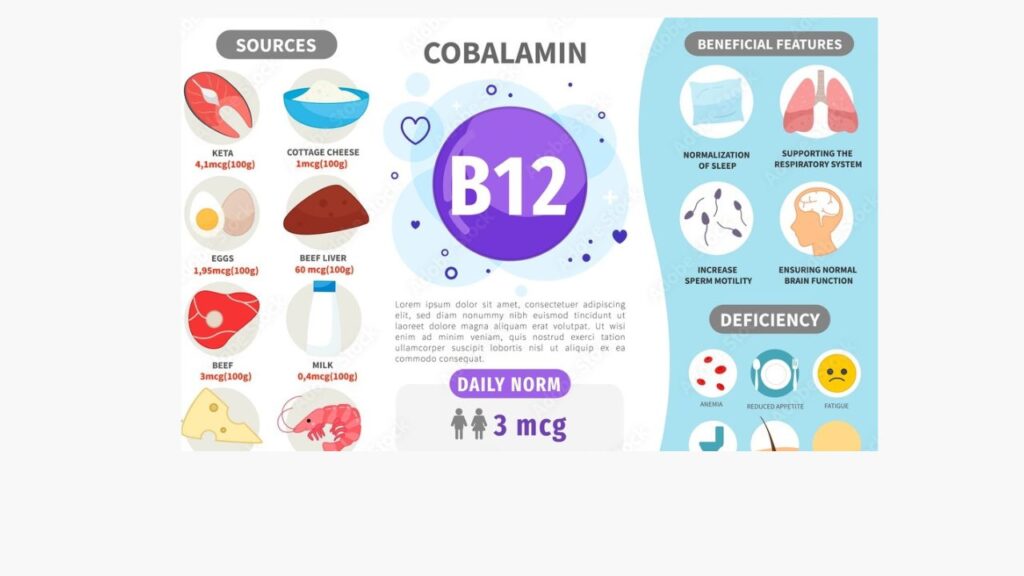
- Vitamin B12 know as Cobalamin, plays important role in keeping our bodies healthy and full of energy.
- It is important for the production of red blood cells, Energy Production, Brain Health, DNA synthesis, nerve cell function, and energy metabolism.
- This water-soluble vitamin is essential for a variety of bodily functions, and a deficiency can lead to a range of health problems.
Benefits of Vitamin B12
- Boosts Energy: Vitamin B12 helps to convert food into energy.
- Brain Function: It supports healthy brain function, improving memory, concentration, and cognitive skills.
- Red Blood Cells: B12 aids in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout your body, preventing anaemia.
- Heart Health: It lowers homocysteine levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
- Nervous System: B12 maintains a healthy nervous system, reducing the risk of nerve damage and related issues.
- Mood Enhancement: Adequate B12 can improve mood, reducing the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Digestive Health: It aids in the digestion process and helps maintain a healthy gut.
- Skin, Hair, and Nails: B12 promotes healthy skin, hair, and nails, keeping them looking their best.
- DNA Repair: It plays a role in DNA synthesis and repair, supporting overall cell health.
- Supports Vegan Diets: Essential for those on a vegan or vegetarian diet, as it’s mainly found in animal products.
Types of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 diveded in 4 types-
- Methylcobalamin: Helps your brain and nerves work properly.
- Cyanocobalamin: Commonly used in supplements and fortified foods.
- Hydroxocobalamin: Used as a treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Adenosylcobalamin: Helps with energy production in your cells.
Daily Requirement of vitamin B12.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for Vitamin B12 varies based on age, life stage, and specific health conditions.
| Vitamin B12 | Daily Requirement (mcg) |
|---|---|
| Children (1-3 years) | 0.9 |
| Children (4-8 years) | 1.2 |
| Children (9-13 years) | 1.8 |
| Teens (14-18 years) | 2.4 |
| Adults (19 years and older) | 2.4 |
| Pregnant women | 2.6 |
| Breastfeeding women | 2.8 |
Vitamin B12.Rich foods Sources
- Dairy Products: Milk, yoghurt, and cheese can be good sources of vitamin B12. For example, one cup (240 ml) of low-fat milk contains around 1.2 mcg of vitamin B12.
- Clams: Clams are superstars when it comes to vitamin B12. Just 3 ounces of cooked clams provide more than 16 micrograms of vitamin B12, which is over 600% of your daily needs.
- Fortified Cereals: Many breakfast cereals are fortified with Vitamin B12. One serving can give you around 1.5 to 6 micrograms of B12.
- Fish: Particularly fatty fish like salmon, trout, and tuna, have significant amounts of vitamin B12.
- Salmon fish contains about 4.9 mcg per 100-gram serving
- Trout fish provides approximately 4.2 mcg
- Cooked tuna offers around 1.9 mcg.
- Eggs – Eggs are a versatile source of B12. One large egg has about 10% (0.6 mcg) of your daily B12 requirement.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey also contribute to your vitamin B12 intake. A 3-ounce (85 grams) serving of cooked chicken contains about 0.3 mcg of vitamin B12.
Vegan Food sources of vitamin b12
- Fortified Foods: Eat cereals, plant-based milk (like soy or almond milk), and nutritional yeast that have vitamin B12 added.
- B12-Fortified Beverages: Some fruit juices and energy drinks have added vitamin B12. Check the labels!
- Nutritional Yeast: Use nutritional yeast as a seasoning on your food. It has a cheesy flavour and is often fortified with vitamin B12.
- Fortified Plant-Based Spreads: Look for margarines or spreads made from plant oils that have added vitamin B12.
- Mushrooms: Some types of mushrooms, like shiitake and maitake, contain a small amount of vitamin B12.
- Supplements: Take vitamin B12 supplements to make sure you get enough of it.
- Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Some meat substitutes, like veggie burgers or meatless sausages, are fortified with vitamin B12.
Deficiency Disorder
Many Disorder happens when your body doesn’t have enough vitamin B12. Such as-
- Pernicious Anemia.
- Digestive issues like diarrhoea, constipation, or loss of appetite.
- Cognitive difficulties, memory problems, or mood changes.
- Depression.
- Feeling tired and weak.
- Pale skin.
- Shortness of breath.
- Dizziness and light-headedness.
**So, if you’re feeling tired, weak, or having trouble remembering things, it’s a good idea to visit a doctor.**
In this guide, we’ll explain how to treat Vitamin B12 deficiency
Treatment
Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
First, it’s essential to confirm that you have a Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Eat a balanced diet that includes B12-rich foods and take supplements as prescribed.
- Dietary Changes.
- Shots (Injections)- In some cases, when the deficiency is very severe, you may need vitamin B12 injections.
- Sometimes, vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by underlying medical conditions, like pernicious anaemia. Treating these underlying conditions is essential for long-term management.
**If you suspect a vitamin B12 deficiency, it’s important to seek medical advice for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.**
READ ALSO….. Vitamin A Benefits And Rich Diet Sources.
commonly Questions Asked Vitamin B12 Related
Q.1. How much vitamin b12 should take?
Ans. – Daily intake of vitamin B12 depends on your age, gender, and work. For most adults, it’s recommended to get 2.4 micrograms (mcg) per day.
Q.2. How to get vitamin b12 naturally?
Ans.- To get vitamin B12 naturally, include foods like meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals in your diet.
Q.3. ICD 10 Code for vitamin b12 deficiency?
Ans.- ICD-10 code for vitamin B12 deficiency: D51.9
Q. 4 Can vitamin b12 deficiency be a sign of cancer?
Ans.- Not everyone with a B12 deficiency has cancer, but it’s worth getting checked out to be sure. So, if you have low B12 levels, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
Q.5. What is Vitamin B12 Shot?
Ans.- It’s a shot, like a small injection shot, is a quick and effective way to boost your body’s supply of vitamin B12.
Q.6. What Side effects to Taking too much vitamin B12 ?
Ans.-Taking too much vitamin B12 can lead to several risks. Always follow recommended doses to avoid these risks.
- Nerve Damage: Excessive B12 can harm your nerves, causing tingling and numbness.
- Digestive Issues: It might upset your stomach, causing diarrhea or cramps.
- Blood Clots: High levels may increase the risk of blood clots.
- Skin Problems: You may develop acne or rashes.
- Kidney Stones: B12 excess can contribute to kidney stone formation.
- Iron Absorption: It might hinder the absorption of essential iron.
- Masking Deficiencies: It can hide other health issues by masking symptoms.